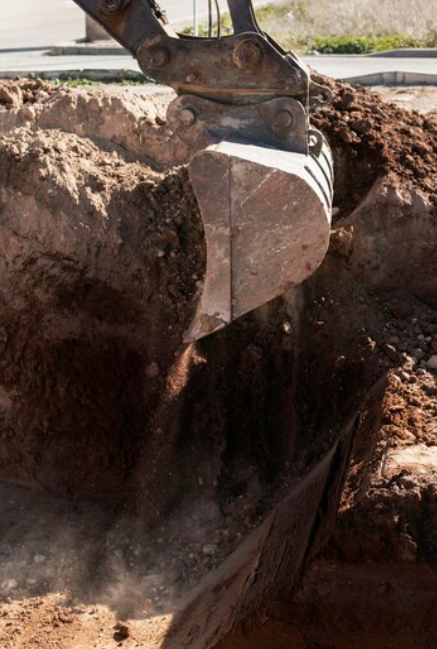
Underground locates are critical to ensuring safety on construction sites, particularly during excavation or any ground-disturbing activities. The process involves identifying and marking the presence of underground utilities such as gas lines, water pipes, electrical cables, and telecommunications lines. Failure to perform proper underground locates can lead to severe consequences, including injury, death, property damage, and significant financial losses. This safety talk will cover the importance of underground locates, the steps involved, common hazards, and best practices for safe excavation.
Understanding Underground Locates
Before any excavation or digging, it’s vital to know what lies beneath the surface. Underground utilities are the lifelines of modern infrastructure, providing essential services like electricity, water, gas, and communications. These utilities are often buried just a few feet below the ground, and striking them can have catastrophic results.
Underground locates are the first line of defense in preventing accidents during excavation. The process involves:
1. Identifying the Utilities: Utilities are mapped out, and their locations are marked on the surface using color-coded flags, paint, or stakes. These markings indicate the type of utility and its approximate location.
2. Communication: Before starting any excavation, it’s crucial to contact the appropriate utility companies or a designated one-call center (such as 811 in the United States). They will send out professionals to mark the underground utilities in the area where the work is planned.
3. Verification: After the utilities have been marked, it’s essential to verify the accuracy of the locate information. This can be done by comparing the markings with utility maps or using additional tools like ground-penetrating radar (GPR) or electromagnetic equipment.
Common Hazards Associated with Underground Locates
Despite careful planning, several hazards can arise during excavation activities. Understanding these risks can help mitigate potential dangers:
1. Striking Utilities: The most obvious hazard is striking a utility line. Hitting a gas line can lead to explosions and fires, while cutting an electrical cable can cause electrocution or power outages. Damaging water or sewage pipes can lead to flooding, contamination, or service interruptions.
2. Inaccurate Locates: Locates are not always 100% accurate. Changes in utility routes, outdated maps, or human error can result in incorrect markings. This is why verification and cautious digging are essential.
3. Unmarked Utilities: Not all utilities may be marked, especially if they were installed privately or without proper documentation. This increases the risk of accidental strikes.
4. Environmental Hazards: Excavating in areas with unstable soil, high groundwater levels, or other environmental challenges can increase the risk of cave-ins, flooding, or soil contamination.
Best Practices for Safe Excavation

To minimize the risks associated with underground locates and ensure a safe excavation process, the following best practices should be adhered to:
1. Plan Ahead: Before any digging begins, conduct a thorough site assessment. Understand the scope of the work, identify potential hazards, and develop a comprehensive excavation plan. This plan should include information about the depth of the excavation, the type of soil, and any known utilities.
2. Contact Utility Companies Early: Contact the appropriate one-call center or utility companies well in advance of the excavation. In some regions, this is a legal requirement. Ensure that all utilities in the area are accounted for and that the markings are clear and accurate.
3. Use Proper Equipment: Utilize appropriate tools for locating underground utilities, such as GPR, electromagnetic locators, or hydro excavation equipment. These tools can help detect utilities that may not be marked or are inaccurately located.
4. Excavate with Caution: When digging near marked utilities, use hand tools or non-destructive methods like vacuum excavation to expose the utility lines. Keep heavy machinery at a safe distance until the utilities are fully exposed and identified.
5. Verify and Monitor: Continuously verify the location of utilities during excavation. If there is any doubt about the accuracy of the markings, stop work immediately and reassess the situation. Monitoring the excavation site regularly can help identify any emerging hazards.
6. Train Your Team: Ensure that all workers involved in the excavation are properly trained in underground locate procedures and understand the importance of following safety protocols. Regular safety meetings and refresher courses can help keep safety at the forefront.
7. Document Everything: Keep detailed records of the locate process, including the time and date of utility markings, the tools used for verification, and any issues encountered. This documentation can be invaluable in the event of an incident or for future reference.
8. Stay Updated on Regulations: Safety regulations regarding underground locates and excavation are constantly evolving. Stay informed about local, state, and federal requirements to ensure compliance and reduce liability.
9. Have an Emergency Plan: In the event of an accidental strike, have an emergency response plan in place. This plan should include steps for evacuating the area, contacting emergency services, and shutting off the affected utility.
Conclusion
Underground locates are a crucial part of any excavation project. By understanding the importance of locating underground utilities and following best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and ensure a safe working environment. Remember, the key to a successful excavation is preparation, communication, and vigilance. Never assume you know what’s below—always verify and proceed with caution.
“Start Your Website Journey Today – Exclusive Hostinger Discounts!”