Safety Performance Measurement is the process of assessing workplace safety using key indicators to track and improve safety performance. These measurements help organizations identify risks, reduce workplace incidents, and enhance overall safety culture.

Types of Safety Performance Measurements:
- Lagging Indicators (Reactive Measures)
- These metrics focus on past incidents and provide insight into the effectiveness of safety programs. Examples include:
- Total Recordable Incident Rate (TRIR) – Measures overall workplace injuries.
- Lost Time Incident Rate (LTIR) – Tracks injuries causing lost workdays.
- Days Away, Restricted, or Transferred (DART) Rate – Identifies serious injuries that impact work.
- Fatality Rate – Measures workplace deaths.
- These metrics focus on past incidents and provide insight into the effectiveness of safety programs. Examples include:
- Leading Indicators (Proactive Measures)
- These focus on preventing accidents before they happen by identifying risks and promoting safety practices. Examples include:
- Near Miss Frequency Rate – Tracks unsafe events that didn’t result in injury.
- Unsafe Act & Unsafe Condition Rate – Measures reported workplace hazards.
- Safety Training Rate – Ensures employees are trained on safety procedures.
- These focus on preventing accidents before they happen by identifying risks and promoting safety practices. Examples include:
- Financial & Insurance-Based Metrics
- These metrics reflect the financial impact of workplace safety. Examples include:
- Experience Modification Rate (EMR) – Determines a company’s insurance costs based on past injury claims.
- Severity Rate – Measures the impact of incidents on productivity through lost workdays.
- These metrics reflect the financial impact of workplace safety. Examples include:
Terminology:
IS:3786 defines as under :
Accident : An unintended occurrence arising out of and in the course of employment of a person
resulting in an injury.
Death: Fatality resulting from an accident
Disability Injury (Lost Time Injury) : An injury causing disablement extending beyond the day
of shift on which the accident occurred.
Non-disabling Injury: An injury which requires medical treatment only, without causing any
disablement whether of temporary or permanent nature.
Reportable Disabling Injury (Reportable Lost Time Injury) : An injury causing death or
disablement to an extent as prescribed by the relevant statute (viz. the Factories Act and the ESI Act).
Days of Disablement (Lost Time): In case of disablement of a temporary nature, the number of
days on which the injured person was partially disabled as defined below. In case of death o r disablement
of a permanent nature whether it be partial or total disablement
Partial Disablement: This is of two types; (i) disablement of a temporary nature which reduces
the earning capacity of an employed person in any employment in which he was engaged at the time of
the accident resulting in the disablement and (ii) disablement of a permanent nature which reduces his
earning capacity in every employment which he was capable of undertaking at the time.
Total Disablement: Disablement, whether of a temporary or permanent nature, which
incapacitates a workman for all work which he was capable of performing at the time of the accident
resulting in such disablement,
Man-hours Worked: The total number of employee-hours worked by all employees working in
the industrial premises. It includes managerial, supervisory, professional, technical, clerical and other
workers including contractors’ labour.
Man-hours worked shall be calculated from the pay roll or time clock record including overtime.
When this is not feasible, the same shall be estimated by multiplying the total man-days worked for the
period covered by the number of hours worked per day. The total number of man-days for a period is die
sum of the number of persons at work on each day of the period. If the daily hours vary from department
to department, separate estimates shall be made for each department and the result added together. When
actual man-hours are not used, the basis on which the estimates are made shall be indicated.
Scheduled or Time Charge: For charges or equivalent man-days lost for death or total
disablement see Part-A and for partial disablement see Part-B of Appendix-A of IS: 3786. For death or total (100%) disablement, equivalent man-days lost are specified as 6000.
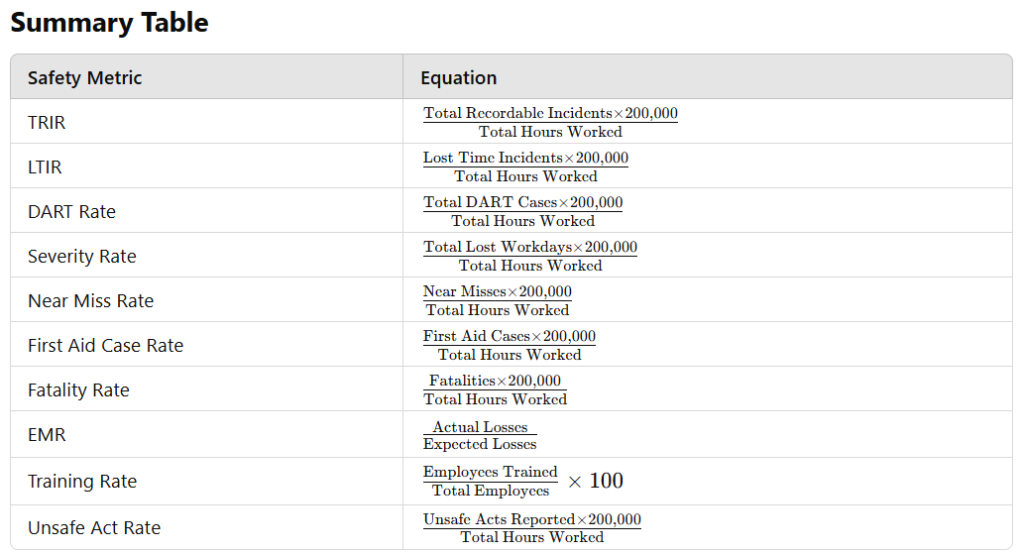
Safety Performance Rates :
Here’s a list of key Safety Performance Rates (Indicators) along with their equations and examples:
Total Recordable Incident Rate (TRIR)
Definition: TRIR measures the number of OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) recordable workplace injuries and illnesses per 100 full-time workers in a given year. It helps companies track overall workplace safety and compare performance with industry standards.

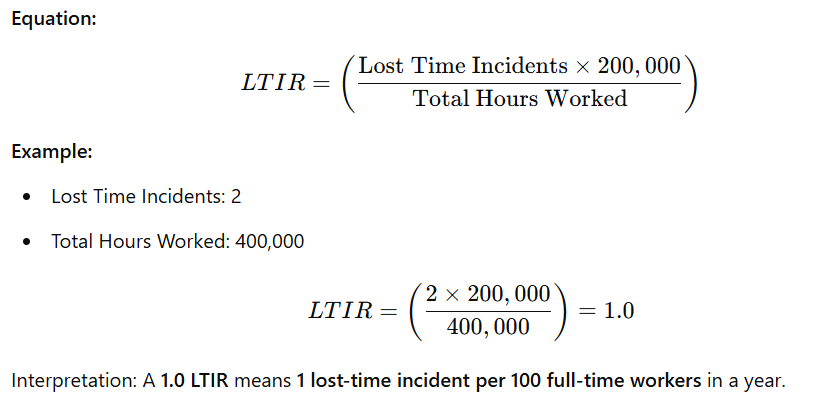
Lost Time Incident Rate (LTIR)
Definition: LTIR calculates the number of workplace injuries or illnesses that result in employees being unable to work for one or more days, per 100 full-time workers annually. It indicates the severity of incidents affecting employee productivity.
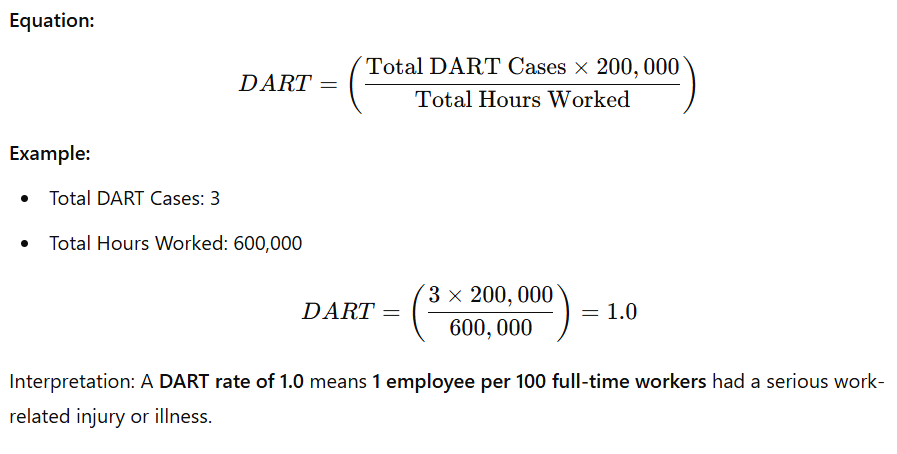
Days Away, Restricted, or Transferred (DART) Rate
Definition: DART rate measures the number of work-related incidents that led to an employee taking days off, being placed on restricted work duties, or being transferred to another job, per 100 full-time employees annually. It reflects the impact of workplace injuries on operations.
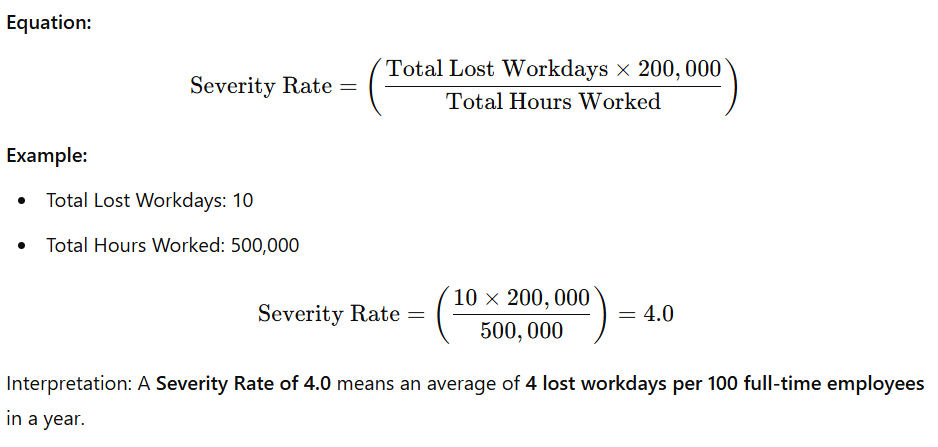
Severity Rate
Definition: Severity rate quantifies the average number of lost workdays due to workplace injuries per 100 full-time workers. It helps organizations understand the seriousness of workplace incidents and their impact on productivity.
Near Miss Frequency Rate
Definition: This rate tracks the number of reported near misses (hazardous events that did not result in injury but had the potential to do so) per 100 full-time workers. It serves as a proactive measure of workplace safety before actual injuries occur.

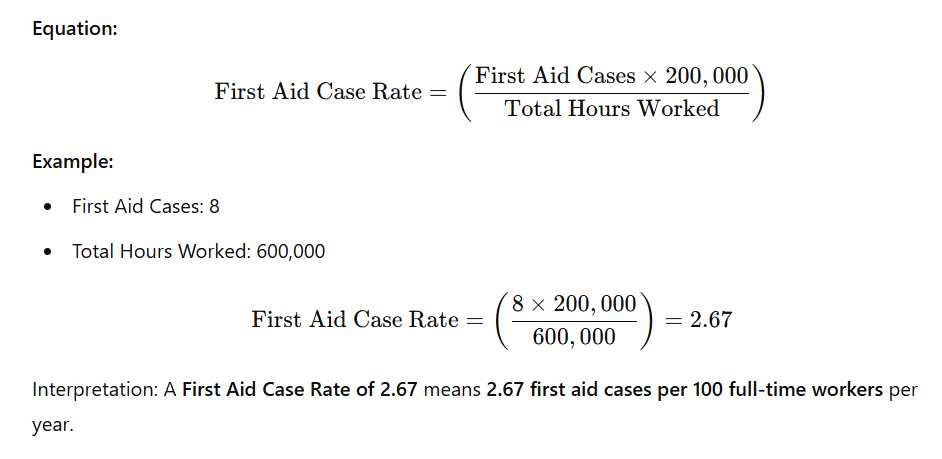
First Aid Case Rate
Definition: First Aid Case Rate represents the number of minor injuries that required only first aid treatment (not recordable by OSHA) per 100 full-time employees. It helps companies monitor minor incidents before they escalate into serious injuries.
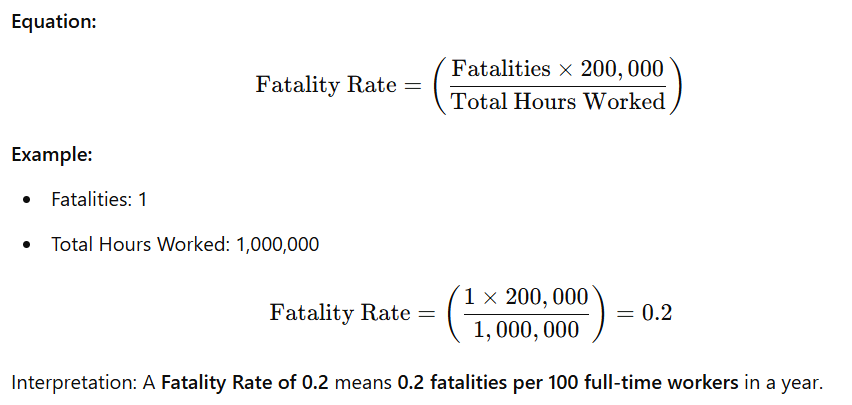
Fatality Rate
Definition: The fatality rate indicates the number of workplace deaths per 100 full-time workers in a given year. It is a critical metric used to measure the most severe workplace incidents.
Experience Modification Rate (EMR)
Definition: EMR is a rating assigned by insurance providers that compares a company’s past workplace injury claims to similar businesses in the industry. A score of 1.0 is average, while a score below 1.0 indicates better safety performance, and a score above 1.0 suggests higher risk and insurance costs.

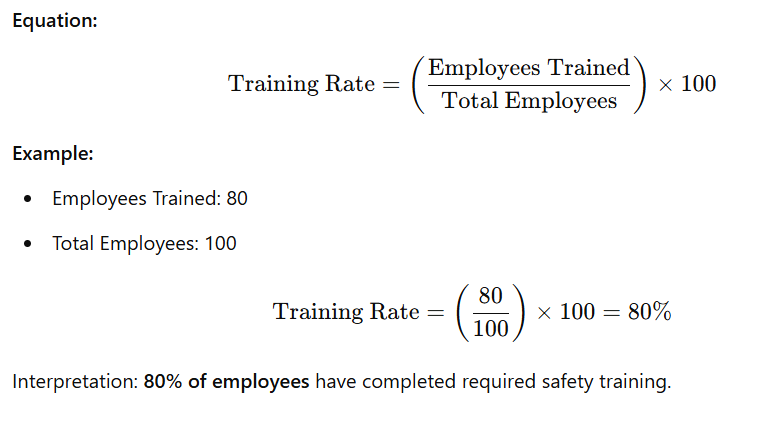
Safety Training Rate
Definition: The Safety Training Rate measures the percentage of employees who have successfully completed workplace safety training programs. It ensures that workers are adequately trained to follow safety protocols and minimize hazards.
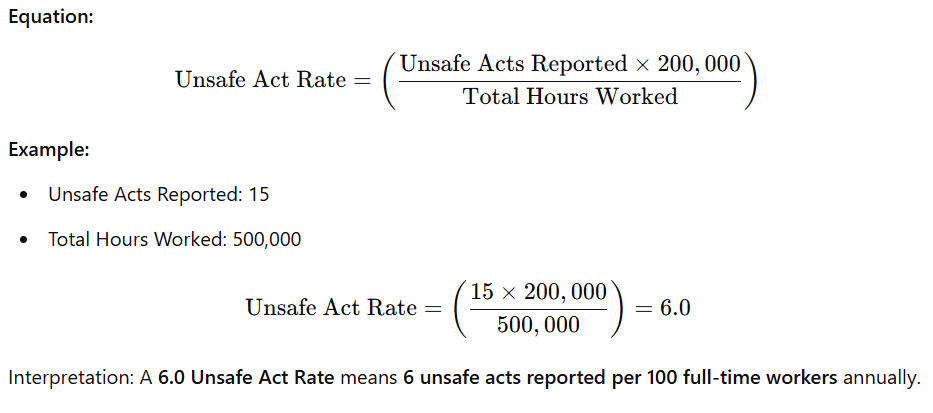
Unsafe Act & Unsafe Condition Rate
Definition: This rate measures the number of unsafe acts (e.g., not wearing PPE, bypassing safety rules) and unsafe conditions (e.g., faulty equipment, exposed wires) reported in the workplace per 100 full-time workers. It helps identify risks before they cause accidents.
Conclusion:
Measuring safety performance allows organizations to track progress, comply with safety regulations, and improve workplace safety standards. A balanced approach using both leading and lagging indicators helps reduce risks and promote a strong safety culture.
“Start Your Website Journey Today – Exclusive Hostinger Discounts!”










