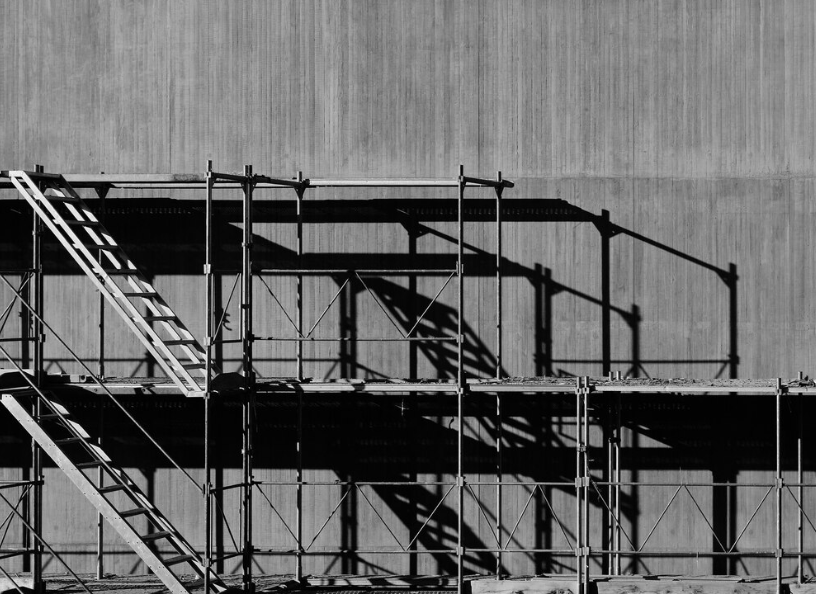
Introduction:
As a safety officer, ensuring the integrity of scaffolding structures is critical to preventing workplace accidents. Scaffolds, when properly assembled and maintained, provide a secure platform for workers at elevated heights. However, the structural components—such as frames, braces, couplers, and supports—must meet safety standards to ensure stability and load-bearing capacity. In this blog, we’ll discuss the importance of understanding and inspecting these key structural components, as well as the essential practices for maintaining a safe working environment. Prioritizing scaffold safety can make the difference between a secure workday and a hazardous situation.
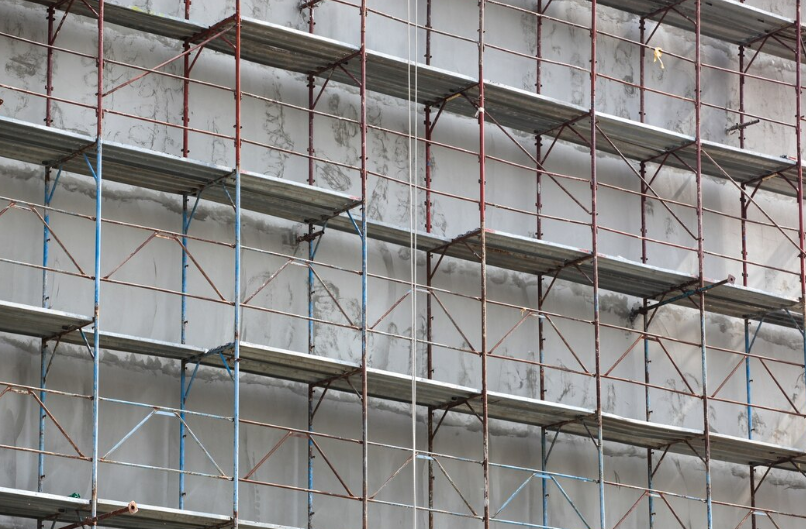

20 Scaffold Safety Talk Points: Structural Components
1. Foundation Stability: Ensure scaffolds are built on a stable, level surface capable of supporting the intended load.
2. Load Capacity: Know the maximum load capacity of the scaffold and avoid exceeding it, including workers, tools, and materials.
3. Inspection Before Use: Inspect all scaffold components, including frames and braces, for defects such as cracks, rust, or wear before each use.
4. Proper Assembly: Follow manufacturer guidelines for assembling scaffolding, using compatible components to prevent structural failures.
5. Securing Base Plates and Mud Sills: Always use base plates and mud sills to distribute weight evenly and prevent sinking or shifting.
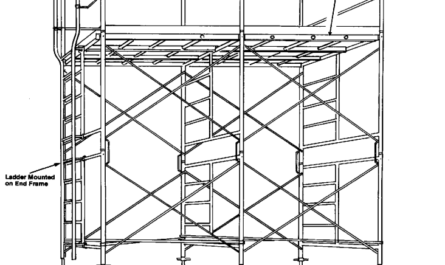
6. Bracing for Stability: Ensure all braces and cross-bracing are securely fastened to provide structural rigidity and prevent swaying.
7. Using the Right Couplers: Only use manufacturer-approved couplers to connect scaffold components and avoid makeshift materials.
8. Guardrails: Install guardrails, midrails, and toeboards on all open sides to prevent falls from elevated work platforms.
9. Proper Support for Decking: Ensure scaffold planks or decks are supported on all ends by the scaffold structure, with no overhang that could cause tipping.
10. Tying Scaffold to the Building: Secure scaffolds to a permanent structure, especially for scaffolds taller than four times their base width, to prevent tipping.
11. Maintaining Structural Integrity: Replace any damaged or compromised parts immediately to maintain the scaffold’s overall strength.
12. Avoid Modifications: Never modify scaffold components or use incompatible parts; always stick to the manufacturer’s approved configuration.
13. Even Weight Distribution: Distribute loads evenly across the scaffold platform to avoid overloading specific areas and causing collapse.
14. Proper Use of Outriggers: Use outriggers when necessary to increase the base width and stabilize taller scaffolds.
15. Weather Considerations: Monitor scaffold structures in high winds or adverse weather, as they can affect the stability of scaffold components.
16. Access Points: Ensure safe access to scaffolds via ladders or built-in steps; climbing cross braces or frames is prohibited.
17. Fall Protection Systems: Utilize appropriate fall protection systems, including harnesses and lanyards, especially on scaffolds over 10 feet high.
18. Maintaining Clear Pathways: Keep scaffold pathways clear of debris, tools, or materials that could cause slips, trips, or falls.
19. Regular Competent Person Inspections: Assign a competent person to inspect scaffolding regularly for safety compliance and any signs of structural weakening.
20. Training and Awareness: Provide scaffold safety training for all workers, including understanding load capacities, proper assembly, and fall protection requirements.
“Start Your Website Journey Today – Exclusive Hostinger Discounts!”